MR

The magnetic resonance imaging research group is part of the Dongguk University. As we have collaborated numerous universities and hospitals in nationwide, we collected a number of high-quality MR images from clinical fields for studies aiming better diagnosis/treatment and prognosis. Based on the collected medical images, we are constructing the standardized database.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive medical imaging and generally used to acquire anatomical images in clinical fields. However, there are various MR techniques that capture functional and metabolic responses, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). With a MRI scanner, we can acquire numerous types of MRI from anatomical imaging to functional/metabolic imaging by applying various MR sequences.
After acquisition of MR images, quality assurance (QA) of acquired images should be performed through signal to noise ratio (SNR), contrast to noise ratio (CNR) and signal uniformity to ensure the acquisition of optimal images. The MR images underwent QA are further processed such as normalization and segmentation to induce more standardized images and to answer specific clinical questions.
After acquisition of MR images, quality assurance (QA) of acquired images should be performed through signal to noise ratio (SNR), contrast to noise ratio (CNR) and signal uniformity to ensure the acquisition of optimal images. The MR images underwent QA are further processed such as normalization and segmentation to induce more standardized images and to answer specific clinical questions.
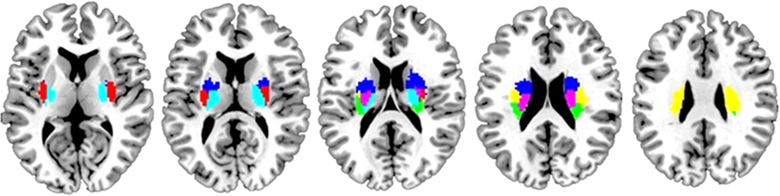
For a clinical aspect, our research group has particularly focused on the data acquisition and analysis in clinical magnetic resonance imaging including T1/T2 anatomical imaging, diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Based on standardised MRI database that we are constructing, we investigate the pathology of neurological diseases using brain mapping methods. We propose neuroimaging markers that predict disease progression and lesion-related brain parcellation that reflects pathology in stroke patients.
T1 Anatomical Image
Tissue including high fat shows in bright while compartments with water shows in dark
T2 Anatomical Image
Water signal is enhanced in T2 anatomical image. Compartments with water are represented in bright
Diffusion Weighted Imaging
Random Brownian motion of water in a tissue voxel is used to generate images
Susceptibility Weighted Imaging
Difference of magnetic susceptibility in tissue is used to produce images
For a clinical aspect, our research group has particularly focused on the data acquisition and analysis in clinical magnetic resonance imaging including T1/T2 anatomical imaging, diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI). Based on standardised MRI database that we are constructing, we investigate the pathology of neurological diseases using brain mapping methods. We propose neuroimaging markers that predict disease progression and lesion-related brain parcellation that reflects pathology in stroke patients.
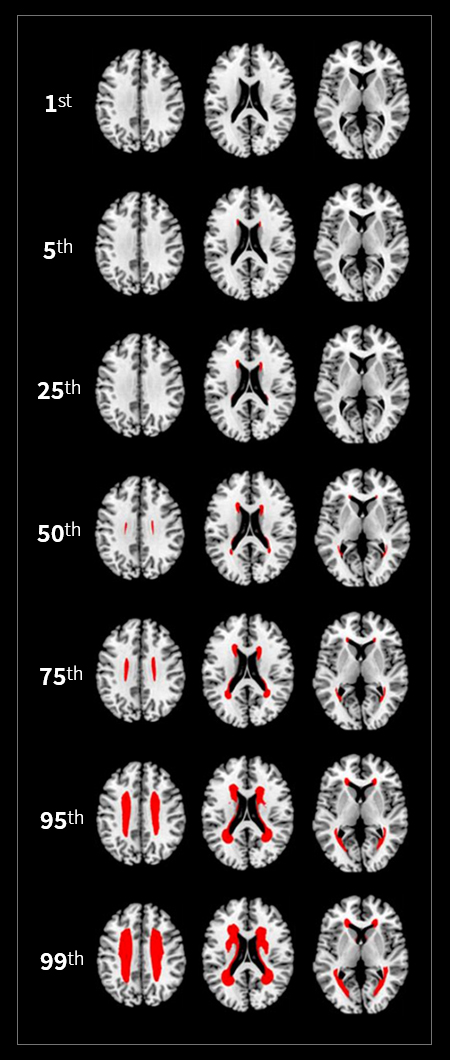
[ Frequency-Volume Maps for Grading the Relative (% Rank) Severity of WMH ]
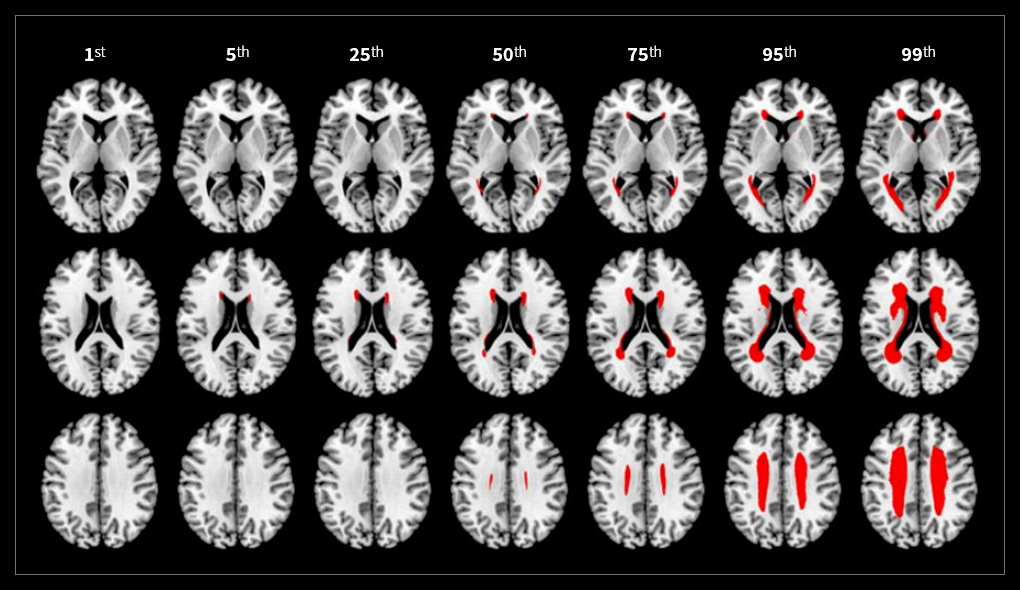
[ Frequency-Volume Maps for Grading the Relative (% Rank) Severity of WMH ]
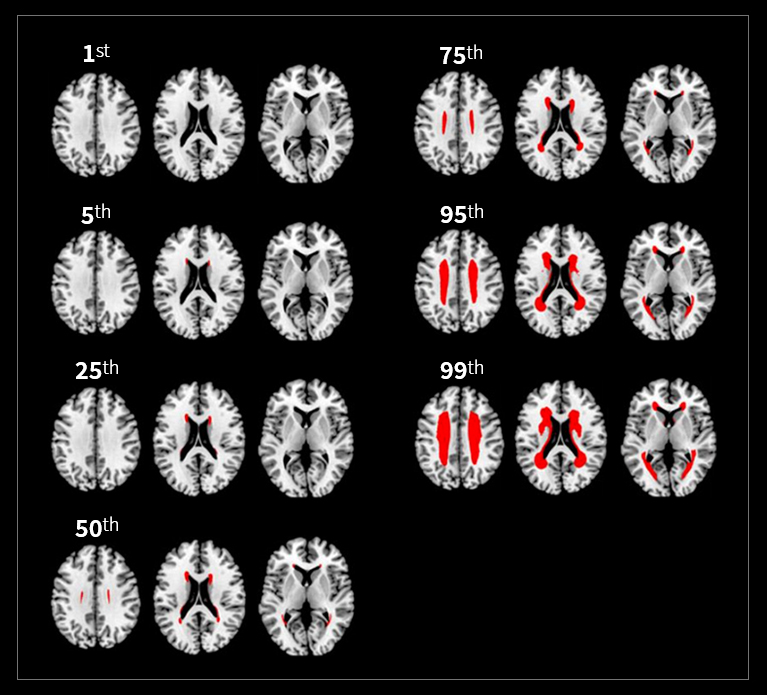
[ Frequency-Volume Maps for Grading the Relative (% Rank) Severity of WMH ]